Overview
Central sensitization is a condition of the nervous system that is associated with the development and maintenance of chronic pain1. It is a pathophysiological process in which the central nervous system undergoes changes that alter its processing of pain and other sensory stimuli2.
When central sensitization occurs, the nervous system goes through a process called wind-up and gets regulated in a persistent state of high reactivity1. This persistent state of reactivity lowers the threshold for what causes pain and subsequently comes to maintain pain even after the initial injury might have healed1.
Central sensitization has two main characteristics:
- Allodynia: A condition where a person experiences pain with things that are normally not painful. For example, chronic pain patients often experience pain even with things as simple as touch or massage1.
- Hyperalgesia: An increased sensitivity to pain3.
In central sensitization, the central nervous system undergoes structural, functional, and chemical changes that make it more sensitive to pain and other sensory stimuli2. This provides an explanatory framework for various frequently encountered conditions2. Patient education about pain physiology and central sensitization can improve quality of life and functional status, and reduce anxiety2.
More Detailed Explanation
- What is Central Sensitization?: When central sensitization occurs, the nervous system goes through a process called wind-up and gets regulated in a persistent state of high reactivity1. This persistent, or regulated, state of reactivity lowers the threshold for what causes pain and subsequently comes to maintain pain even after the initial injury might have healed1.
- Characteristics: Central sensitization has two main characteristics. Both involve a heightened sensitivity to pain and the sensation of touch. They are called allodynia and hyperalgesia1. Allodynia occurs when a person experiences pain with things that are normally not painful. For example, chronic pain patients often experience pain even with things as simple as touch or massage1. Hyperalgesia is an increased sensitivity to painful stimuli1.
- Changes in the Nervous System: In central sensitization, the central nervous system undergoes structural, functional, and chemical changes that make it more sensitive to pain and other sensory stimuli2. This process is often referred to as the “wind-up” phenomenon1.
- Role in Chronic Pain: Central sensitization is a key mechanism in the development of chronic pain1. It provides an explanatory framework for various frequently encountered conditions2. Patient education about pain physiology and central sensitization can improve quality of life and functional status, and reduce anxiety and catastrophization2.
- Treatment: Cognitive behavior therapy aims to reframe negative thoughts, emotions, and behaviors as positive ones2. When patients have chronic pain or other symptoms that seem out of proportion to anything we can tell is physically wrong with them, we should not assume they are faking it2. The central nervous system can undergo changes---structural, functional, and chemical---that make it more sensitive to stimuli, a process called central sensitization2.
Remember, central sensitization is a complex process that plays a significant role in the perception and maintenance of chronic pain1. Understanding this process can help in the management of chronic pain conditions2.
Central Sensitization Video
ONE SENTENCE SUMMARY:
Central sensitization is a condition where the brain becomes overly sensitive to pain signals, making even mild sensations feel intense and overwhelming.
MAIN POINTS:
- The brain receives many calls from the nervous system every day, prioritizing threats over non-threatening sensations.
- In central sensitization, the brain becomes hyper-alert, treating even minor stimuli as danger signals.
- This condition is characterized by increased pain processing in the brain, leading to symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and depression.
- Central sensitization cannot be medicated away or relieved through medical procedures; instead, it requires rewiring the brain through behavioral changes.
TAKEAWAYS:
- The brain can rewire itself throughout life, creating new pathways and connections.
- Behavior plays a crucial role in maintaining or reversing central sensitization.
- Adopting healthy behaviors that soothe the central nervous system can help alleviate symptoms of central sensitization.
- With proper training, people with central sensitization can reduce their pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Non-Pharmacological Treatment Methods
mayoclinic.org/patient-education?PLID=0_bwqmjzbr
ONE SENTENCE SUMMARY:
Learning non-pharmacological methods, such as deep breathing, guided imagery, consistent routines, and social support, helps manage chronic pain, restore physical function, and improve overall well-being.
MAIN POINTS:
- Chronic pain can lead to significant physical and emotional decline.
- Conventional treatments were ineffective, necessitating exploration of alternative methods.
- Techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery help manage pain.
- Restoring normal sleep patterns is essential for recovery.
- Establishing a daily routine promotes healthy habits and self-care.
- Regular physical activity is important, even with chronic pain.
- Occupational therapy helps resume enjoyable activities without worsening symptoms.
- Social interactions and support groups offer emotional stability and encouragement.
- Achieving small goals and finding new passions can improve motivation and happiness.
- The brain’s interpretation of pain signals influences perception.
TAKEAWAYS:
- Deep breathing and guided imagery effectively reduce stress, anxiety, and pain.
- Consistently practicing self-care routines and physical activity is crucial for managing chronic pain.
- Aiming for a regular sleep schedule enhances overall health and pain management.
- Engaging in social activities and seeking support from others can boost emotional well-being.
- Setting achievable goals and discovering new passions can significantly improve quality of life.
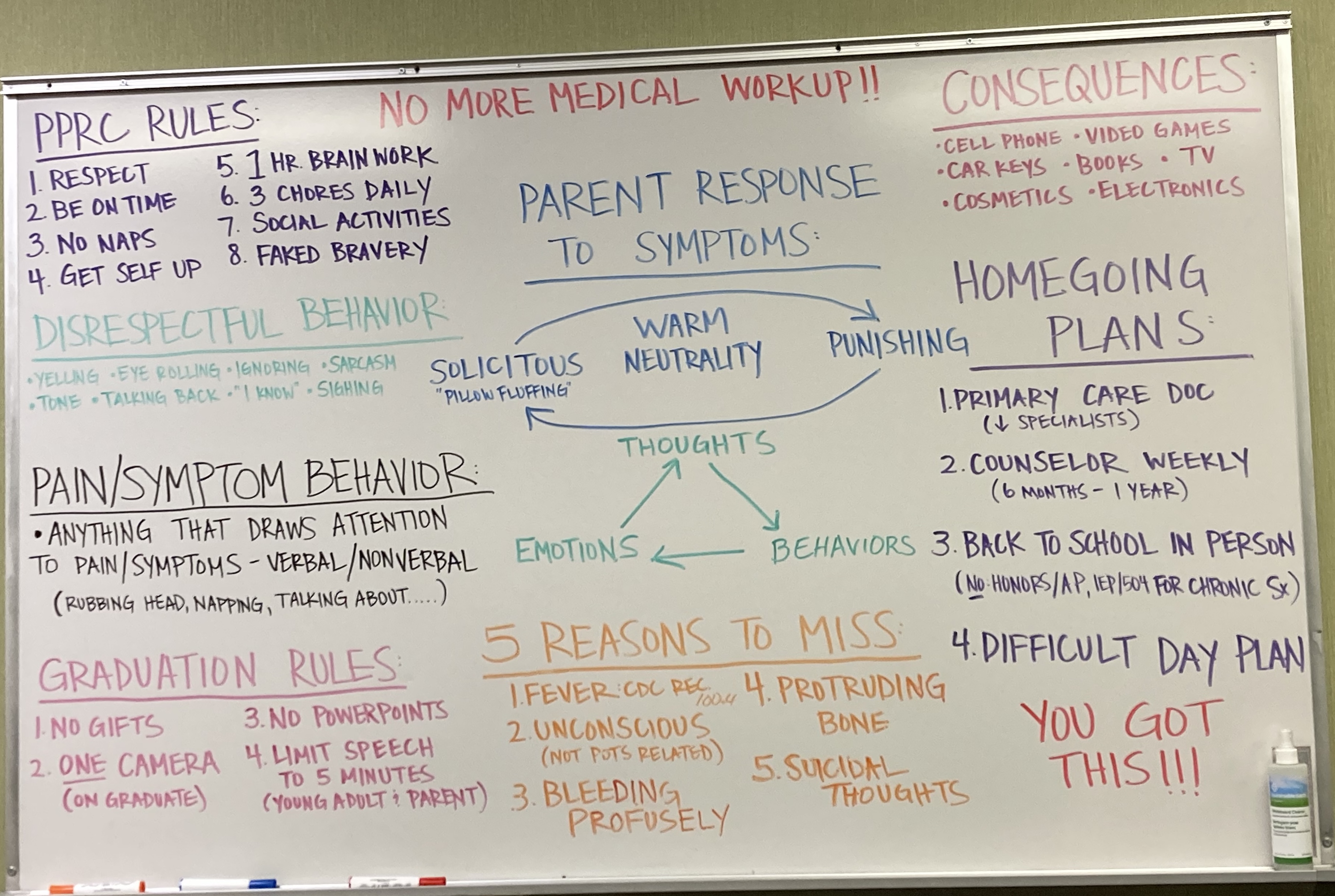
PRC Rules Dashboard
Resources
- Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine: They have a comprehensive review on central sensitization, chronic pain, and other symptoms1. This source provides a better understanding and management of the condition.
- The Lancet: This is a highly respected medical journal that has published articles discussing the causes, therapies, and terminology related to central sensitization2.
- Wiley Online Library: They have published articles on the neurobiology of central sensitization3.
- Mayo Clinic: They have resources describing the pathophysiology of central sensitization4.
Published Papers
- “Central sensitization, chronic pain, and other symptoms: Better understanding, better management”: This paper, published in the Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, discusses the pathophysiological process of central sensitization and its role in various conditions where patients have unexplained pain and fatigue1.
- “Central sensitisation: causes, therapies, and terminology”: This correspondence, published in The Lancet, discusses the potential of central sensitization for precision medicine in rheumatology2.
- “Research on central sensitization of endometriosis-associated pain”: This review aims to systematically synthesize the literature published to date regarding the central sensitization mechanism of endometriosis-associated pain3.
- “PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CENTRAL SENSITIZATION”: This paper defines central sensitization and recognizes common central sensitization syndromes. It also describes microscopic neurological mechanisms leading to central sensitization4.
- “Central Sensitization in Humans: Assessment and Pharmacology”: This paper discusses how human experimental pain models and quantitative sensory testing (QST) can be used to profile the efficacy of new drugs5.
These papers provide a comprehensive understanding of central sensitization, its causes, effects, and potential treatments.